A geographic information system (GIS) is a computer based tool for mapping and analyzing things that exist and events that happen on earth. GIS technology integrates common database operation such as query and statistical analysis with the unique visualization and geographic analysis benefits offered by maps.
These abilities distinguish GIS from other information systems and make it valuable to a wide range of public and private enterprises for explaining events, predicating outcomes, and planning strategies.How does it (GIS) work?GIS stores information about the world as a collection of thematic layers that can be linked together by geography. This simple but extermly powerful and versatile concept has proven invaluable for solving many real-world problems from tracking delivery vehicles, to recording details of planning applications, to modeling global atmospheric circulation.
Geographic References:
Geographic information contains either an explicit geographic reference, such as a latitude and longitude or national grid coordinate, or an implicit reference such as an address, postal code, census tract name, forest stand identifier, or road name. An automated process called geocoding is used to create explicit geographic references from implicit references. These geographic references allow you to locate features, such as a business or forest stand, and events, such as an earthquake, on the earth's surface for analysis.
Vector and Raster Model:
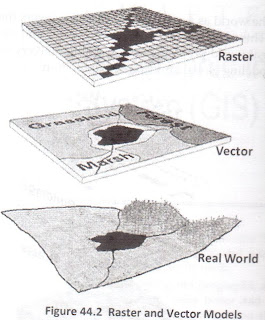
GIS work with two fundamentally different types of geographic models: the 'vector' model and 'raster' model. In the vector model, information about points, lines, and polygons is encoded and stored as a X,Y coordinate. Linear features, such as roads and rivers, can be stored as a collection of point coordinates. Polygonal features, such as sales territories and rivers catchments, can be stored as closed loop of coordinates.
The vector model is extremely useful for describing discrete features, but less useful for describing continuously varying features such as soil type or accessibility costs for hospitals. The raster model has evolved to model such continuous features. A raster image comprises a collection of grid cells rather like a scanned map or pictures. Both are vector and raster models for storing geographic data have unique advantages and disadvantages. Modern GISs are able to handle both models.
Components of GIS:
Geographic References:
Geographic information contains either an explicit geographic reference, such as a latitude and longitude or national grid coordinate, or an implicit reference such as an address, postal code, census tract name, forest stand identifier, or road name. An automated process called geocoding is used to create explicit geographic references from implicit references. These geographic references allow you to locate features, such as a business or forest stand, and events, such as an earthquake, on the earth's surface for analysis.
Vector and Raster Model:
GIS work with two fundamentally different types of geographic models: the 'vector' model and 'raster' model. In the vector model, information about points, lines, and polygons is encoded and stored as a X,Y coordinate. Linear features, such as roads and rivers, can be stored as a collection of point coordinates. Polygonal features, such as sales territories and rivers catchments, can be stored as closed loop of coordinates.
The vector model is extremely useful for describing discrete features, but less useful for describing continuously varying features such as soil type or accessibility costs for hospitals. The raster model has evolved to model such continuous features. A raster image comprises a collection of grid cells rather like a scanned map or pictures. Both are vector and raster models for storing geographic data have unique advantages and disadvantages. Modern GISs are able to handle both models.
Components of GIS:
- Hardware: Hardware is the computer on which a GIS operates. Today, GIS software runs on wide range of hardware types, from centralized computer servers to desktop computers used in stand-aline or networked configurations.
- Software: GIS software provides the functions and tools needed to store, analyze, and display geographic information. Software components are given below:
- Tools for the input and manipulation of geographic information
- a database management system (DBMS)
- tools that support geographic query, analysis, and visualization
- a graphical user interface for easy access to tools.
- Data: Possibly, the most important component of GIS is the data. Geographic data and related tabular data can be collected in house or purchased from a commercial data provider. A GIS will integrate spatial data with other data resources and can even use a DBMS, used by most of organizations to recognize and maintain their data, to manage spatial data.
- People: GIS technology is of limited value without the people who manage the system and develop plans for applying it to real world problems. GIS users range from technical specialists who design and maintain the system to those who use it to help them perform their everyday work.
- Methods: A successful GIS operates according to a well designed plan and business rules, which are the models and operating practices unique to each organization.

3 comments:
Sir,
I am a Geomatics Engineering students at TU WRC, Pokhara. Do you have any idea about online job for us?If you had any such idea please mail me at kdsingh992@gmail.com
I am student of geology. I finished bachelor degree from Tri -chandra collage, kathmandu . I have taken Gis training. If you have such online job on this please inbox be in dhakalshraddha@gmail.com
I am a Geomatics Engineering student at Kathmandu University currently at 4th year .I am good at using GIS and have done several projects using GIS . If you have any kind of Geo spatial related jobs online or Geo spatial projects . please do inform me at my mailing address : achutpandey13@gmail.com
Post a Comment